
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
A hydraulic valve is an automation component operated by pressure oil. The article introduces a total of 17 hydraulic valves in 8 categories! How do these hydraulic valves work? What's the use? After reading these 38 animated pictures carefully, you will understand it!
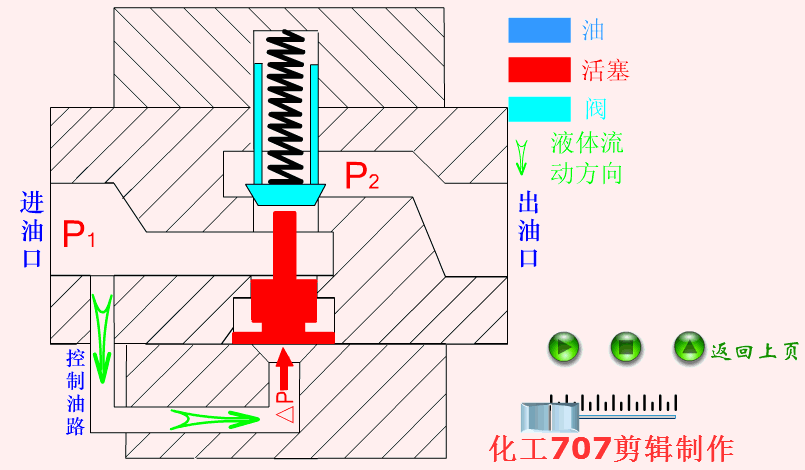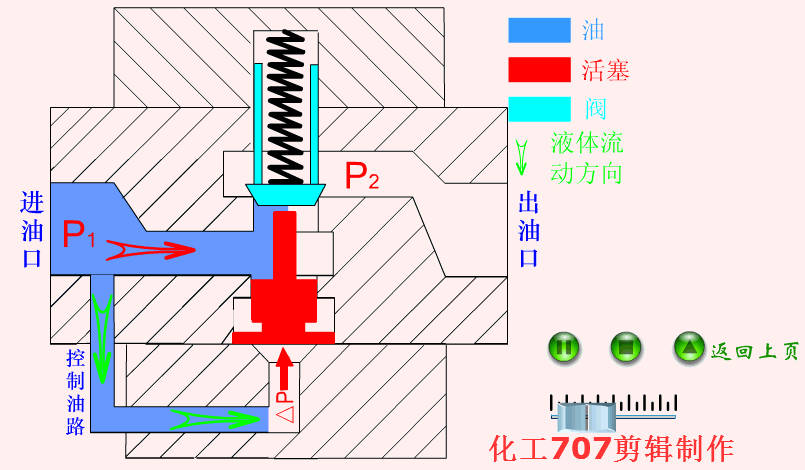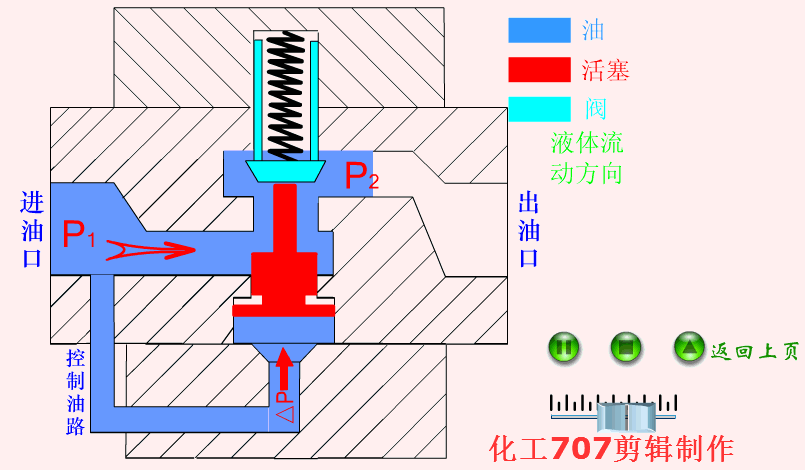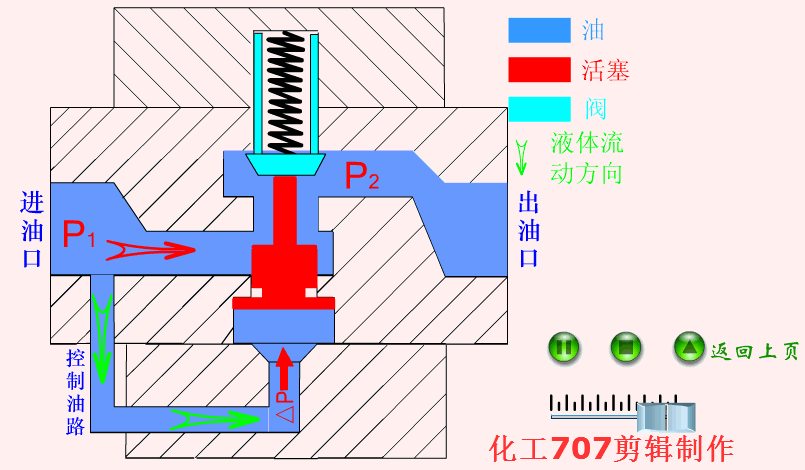
Hydraulic valve: It is an automation component operated by pressure oil. It is controlled by the pressure oil of the pressure distribution valve. It is usually used in combination with an electromagnetic pressure distribution valve. It can be used to remotely control the on and off of the oil, gas, and water pipeline systems of hydropower stations.
Classified by control method: manual, electric control, hydraulic control.
Classified by function: flow valve (throttle valve, speed control valve, diverting and collecting valve), pressure valve (relief valve, pressure reducing valve, sequence valve, unloading valve), directional valve (electromagnetic reversing valve, manual change Valve, one-way valve, hydraulic control one-way valve).
1. One-way valve (2 kinds)
The one-way valve is a one-way valve that fluid can only flow along the water inlet, but the medium at the water outlet cannot flow back.
One-way valve is also called check valve or check valve. Used in hydraulic systems to prevent reverse flow of oil flow, or used in pneumatic systems to prevent reverse flow of compressed air.
When installing a check valve, pay special attention to the flow direction of the medium. The normal flow direction of the medium should be consistent with the direction of the arrow indicated on the valve body, otherwise the normal flow of the medium will be blocked. The bottom valve should be installed at the bottom of the pump suction line.
When the check valve is closed, water hammer pressure will be generated in the pipeline. In severe cases, it will cause damage to the valve, pipeline or equipment. Especially for large-mouth pipelines or high-pressure pipelines, it should be a high-level attention to the check valve selection. .
1

Right angle check valve
2

Straight check valve

When oil is supplied to port A of one-way valve

When oil is supplied to port B of one-way valve

When the check valve has control oil
2. Reversing valve (4 types)
The reversing valve is a directional control valve with more than two flow patterns and more than two oil ports. It is a valve that realizes the communication, cut-off and reversal of hydraulic oil flow, as well as pressure unloading and sequential action control.
This kind of changeover valve has a wide range of applications in petroleum and chemical production, and is most commonly used in synthetic ammonia gas production systems. In addition, the reversing valve can also be made into a flap structure, which is mostly used in small flow situations. When working, only need to turn the hand wheel to change the flow direction of the working fluid through the valve clack.
two
Bit
two
through
Two-position means that the spool is working in two states. When the coil is not energized, the spool is in one position and moves to the other position when energized. The conduction state of the valve is switched by the change of position; the two-way means that the valve has Two interfaces (one in and one out).
The two-position two-way valve is actually a shut-off valve, which has the purpose of shutting off/opening the pipeline and has no reversing function.

two
Bit
four
through
Two-position four-way reversing valve is suitable for dry oil or thin oil centralized lubrication system to change the direction of oil supply or open and close the oil supply pipeline.
This reversing valve uses a high-torque DC geared motor to drive the commutation, so even in harsh working conditions (such as low temperature or high-viscosity grease), the reversing action is very reliable.
During the commutation process, the piston runs at a higher speed in a very short time, reducing reciprocation and avoiding premature wear.
After receiving the commutation signal in the system, the DC motor makes a rotary motion and converts the rotary motion into the linear reciprocating motion of the piston rod through the eccentric wheel. When the piston moves from one end to the other and reaches the required commutation position, the limit switch acts to make the DC motor lose power, and then the motor stops rotating, and the commutation process is completed.

Reversing valve-two-position four-way left position

Directional valve-two-position four-way right position
three
Bit
four
through
P is the oil supply port, O is the oil return port, and A and B are the output ports leading to the actuator.
When the spool is in the neutral position, all oil ports are cut off and the actuator does not move;
When the spool moves to the right position, P communicates with A, and B communicates with O;
When the spool moves to the left position, P is connected to B, and A is connected to O.
In this way, the actuator can move forward and backward.

Directional valve-three-position four-way left position

Directional valve-three-position four-way neutral position

Directional valve-three-position four-way right position
three
Bit
Fives
through

Reversing valve-three-position five-way left position

Reversing valve-three-position five-way neutral position

Directional valve-three-position five-way right position
3. Manual reversing valve (1 type)
The manual reversing valve is a directional control valve that relies on the force of a manual lever to drive the spool to move to achieve the on-off or switching of the oil circuit.
The manual reversing valve plays the same role in the hydraulic system as the electromagnetic reversing valve. It is easy to operate, reliable in work and does not require electricity.

4. Throttle valve (1 kind)
The throttle valve is a valve that controls the flow of fluid by changing the throttle section or throttle length.
The throttle valve has no negative flow feedback function, and cannot compensate for the unstable speed caused by the load change. It is generally only used for occasions where the load change is not large or the speed stability is not high.
The shape and structure of the throttle valve is no different from that of the stop valve, except that the shapes of their opening and closing parts are different. Most of the opening and closing parts of the throttle valve are conical streamlined, and the flow and pressure can be adjusted by changing the cross-sectional area of the channel. The throttle valve is used to reduce the pressure of the medium when the pressure drop is extremely large.
The flow rate of the medium between the throttle valve disc and the valve seat is very large, so that the surface of these parts is quickly damaged-the so-called cavitation phenomenon. In order to minimize the impact of cavitation, the valve disc is made of cavitation resistant material (made of alloy steel) and made into a streamlined cone with a tip angle of 140-180. This can also enable the valve disc to have a larger opening height, which is generally not recommended Throttling under a small gap.

Throttle valve

When the throttle valve opening is large

Throttle opening hours
5. Diverting and collecting valve (1 type)
Diversion and collection valve, also called: synchronization valve, is an independent hydraulic device that integrates the functions of hydraulic diversion valve and collection valve.
There are usually many ways to realize synchronous movement, but among them, the synchronous control hydraulic system using the shunt collecting valve-synchronous valve has many advantages such as simple structure, low cost, easy manufacturing, and strong reliability. Therefore, the synchronous valve is used in the hydraulic system. Wide range of applications.

When the shunting and collecting valve P3>P4

When dividing and collecting valve P3=P4

When dividing and collecting valve P3<P4
Six, sequence valve (4 types)
The sequence valve is a valve that controls the sequence of actuator actions according to the pressure of the circuit in a system with more than two branch circuits.
According to the different assembly structure, sequence valve can realize different circuit functions, such as overflow valve, sequence valve and balance valve.
If the opening and closing characteristics of the sequence valve are too poor, the primary pressure will be too high when the flow is large, and the efficiency of the circuit will decrease. The opening and closing characteristics have hysteresis, the opening pressure is lower than the closing pressure, and attention should be paid when the load flow changes.
Open the valve with too low pressure, and when the pressure is lower than the set pressure, forward leakage will occur, causing the actuator to malfunction. When the flow rate through the valve is much smaller than the rated flow rate, vibration or other instability occurs. At this time, measures must be taken on the loop.

Sequence valve
1

Internal control internal drain sequence valve
2

Internal control and external drain sequence valve
3

External control internal drain sequence valve
4

External control drain type sequence valve
Seven, speed control valve (1 type)
The speed control valve is composed of a fixed differential pressure reducing valve and a throttle valve in series, and is a throttle valve with pressure compensation.
The throttle valve is used to adjust the flow through, and the fixed differential pressure reducing valve automatically compensates for the influence of load changes, so that the pressure difference before and after the throttle valve is a fixed value, eliminating the influence of load changes on the flow.
The pressure before and after the throttle valve is led to the right and left ends of the pressure reducing valve core respectively. When the load pressure increases, the hydraulic pressure acting on the left end of the pressure reducing valve core increases, the valve core moves to the right, and the pressure reducing port Increase the pressure drop, so that the pressure difference (p2-p3) of the throttle valve remains unchanged; vice versa. In this way, the flow rate of the speed control valve is constant (not affected by the load).
The speed control valve can also be designed to throttle first and then decompress.

When the pressure of the governor valve decreases

When the pressure of the speed control valve increases
8. Overflow valve (4 types)
The overflow valve is a hydraulic pressure control valve, which mainly plays the role of constant pressure overflow, voltage stabilization, system unloading and safety protection in hydraulic equipment.
Constant pressure overflow function: In the metering pump throttling adjustment system, the metering pump provides a constant flow. When the system pressure increases, the flow demand will decrease. At this time, the overflow valve is opened to allow excess flow to overflow back to the tank to ensure that the inlet pressure of the overflow valve, that is, the pump outlet pressure is constant (the valve port often opens with pressure fluctuations).
Stabilizing effect: The overflow valve is connected in series on the oil return line, and the overflow valve generates back pressure, which increases the stability of the moving parts.
System unloading function: the solenoid valve with small flow overflow is connected in series to the remote control port of the overflow valve. When the solenoid is energized, the remote control port of the overflow valve is connected to the oil tank, and the hydraulic pump is unloaded at this time. The overflow valve is now used as an unloading valve.
Safety protection function: When the system is working normally, the valve is closed. Only when the load exceeds the specified limit (the system pressure exceeds the set pressure), the overflow is turned on and overload protection is performed to prevent the system pressure from increasing (usually the set pressure of the overflow valve is 10% to 20% higher than the maximum working pressure of the system) ).
The main requirements for the relief valve: large pressure regulation range, small pressure regulation deviation, small pressure swing, sensitive action, large overload capacity, and low noise.

1. Pilot relief valve
Pilot-operated relief valve, which acts on the pressure measuring surface of the main spool and the pilot spool, consists of a pilot and a main valve.
When working, the hydraulic pressure acts on the pressure measuring surface of the main spool and the pilot spool at the same time.
When the pilot valve 1 is not opened, the oil does not flow in the valve cavity, and the pressure acting on the main valve core 6 in the upper and lower directions is equal, but because the effective pressure area A2 of the upper end surface is greater than the effective pressure area A1 of the lower end surface, the main The valve core is in the lowermost position under the action of the resultant force, and the valve port is closed.
When the oil inlet pressure increases to make the pilot valve open, the fluid flows back to the tank through the orifice 5 on the main valve core and the pilot valve 1. Due to the damping effect of the orifice, the hydraulic pressure in the upper and lower directions of the main spool 6 is not equal. The main spool moves up under the action of the pressure difference, opens the valve port, realizes overflow, and maintains the pressure basically stable. . Adjust the pressure regulating spring 9 of the pilot valve to adjust the overflow pressure.

Pilot operated relief valve

Relief valve overflow

When the inlet pressure is not high

When the inlet pressure increases

2. Low pressure relief valve

When the pressure is not high

When the pressure rises

3. Pressure reducing valve
The pressure reducing valve is a valve that reduces the inlet pressure to a certain required outlet pressure through adjustment, and relies on the energy of the medium itself to automatically maintain a stable outlet pressure.
From the point of view of fluid mechanics, the pressure reducing valve is a throttling element whose local resistance can be changed, that is, by changing the throttling area, the flow rate and the kinetic energy of the fluid are changed, resulting in different pressure losses, so as to achieve the purpose of decompression.
Then rely on the adjustment of the control and regulation system to balance the fluctuation of the pressure behind the valve with the spring force, so that the pressure behind the valve remains constant within a certain error range.


4. Cartridge valve
Cartridge valve is different from what we call ordinary hydraulic control valve, its flow can reach 1000L/min, and its diameter can reach 200~250mm.
The spool has simple structure, sensitive action and good sealing performance. Its function is relatively single, mainly to realize the on or off of the hydraulic circuit, and when used in combination with the ordinary hydraulic control valve, it can realize the control of the system oil direction, pressure and flow.

March 31, 2023
March 27, 2023
September 25, 2024
September 24, 2024
Mail an Lieferanten
March 31, 2023
March 27, 2023
September 25, 2024
September 24, 2024

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.